Deploy Nuxt on GitHub Pages
How to deploy Nuxt app on GitHub Pages?
Nuxt gives you the possibility to host your web application on any static hosting like GitHub Pages for example.
To deploy on GitHub Pages, you need to generate your static web application:
yarn generate
npm run generate
It will create a dist folder with everything inside ready to be deployed on GitHub Pages hosting. Branch gh-pages for project repository OR branch master for user or organization site
CNAME file, it is recommended that CNAME file is put in the static directory. More documentation about it.Deploying to GitHub Pages for repository
First of all, you want to make sure to use static target since we are hosting on GitHub pages:
export default {
target: 'static'
}
If you are creating GitHub Pages for one specific repository, and you don't have any custom domain, the URL of the page will be in this format: http://<username>.github.io/<repository-name>.
If you deployed dist folder without adding router base , when you visit the deployed site you will find that the site is not working due to missing assets. This is because we assume that the website root will be /, but in this case it is /<repository-name>.
To fix the issue we need to add router base configuration in nuxt.config.js:
export default {
target: 'static',
router: {
base: '/<repository-name>/'
}
}
This way, all generated path asset will be prefixed with /<repository-name>/, and the next time you deploy the code to repository GitHub Pages, the site should be working properly.
Command line deployment
You can also use push-dir package :
First install it:
yarn add --dev push-dir
npm install push-dir --save-dev
Add a deploy command to your package.json with the branch as gh-pages for project repository OR master for user or organization site.
"scripts": {
"dev": "nuxt",
"generate": "nuxt generate",
"start": "nuxt start",
"deploy": "push-dir --dir=dist --branch=gh-pages --cleanup"
},
Then generate and deploy your static application:
yarn generate
yarn deploy
npm run generate
npm run deploy
Build server deployment
You can take deployment one step further and rather than having to manually compile and deploy the files from your local install, you can make use of a build server to monitor your GitHub repository for new commits and then checkout, compile and deploy everything for you automatically.
GitHub Actions
To deploy via GitHub Actions , the official tool for software automation with GitHub, if you don't have a workflow you need to create a new one or append a new step to your existing workflow.
It uses the GitHub Pages Action which pushes the generated files from the dist folder to your default GitHub Pages branch gh-pages.
With an existing workflow, add the following step:
- name: Deploy
uses: peaceiris/actions-gh-pages@v3
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
publish_dir: ./dist
With a new workflow, paste the following content into a new file called cd.yml in .github/workflows directory:
name: cd
on: [push, pull_request]
jobs:
cd:
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
matrix:
os: [ubuntu-latest]
node: [14]
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@master
- name: Setup node env
uses: actions/setup-node@v2.1.2
with:
node-version: ${{ matrix.node }}
- name: Install dependencies
run: yarn
- name: Generate
run: yarn generate
- name: Deploy
uses: peaceiris/actions-gh-pages@v3
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
publish_dir: ./dist
Then commit this to your repository:
git add .github/workflows/cd.yml
git commit -m "Adding github pages deploy workflow"
git push origin
On completion, you'll see your gh-pages branch updated as well as your site.
Travis CI
To deploy with Travis CI , a free for open source projects build server, sign in via your GitHub account, granting Travis access to view your repositories, and then enable the build server for your repository by toggling the switch next to your repositories name in the list displayed.
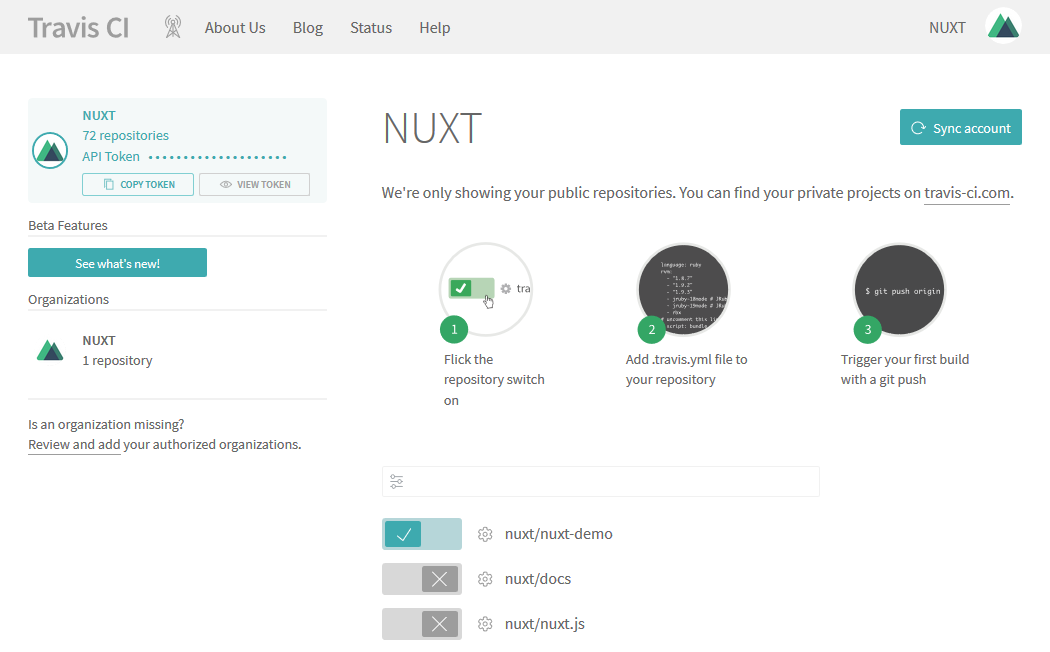
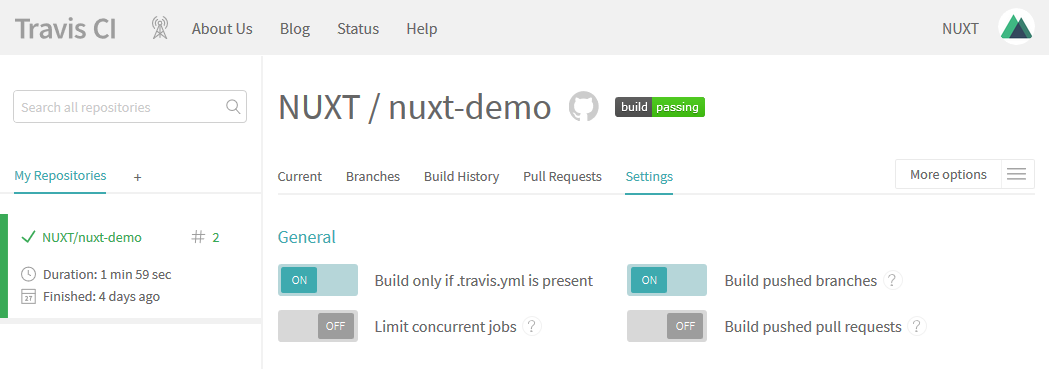
Next, click the cog icon beside your repository name to configure the general settings of the build sever and enable the 'Build only if .travis.yml is present' feature by toggling the switch.
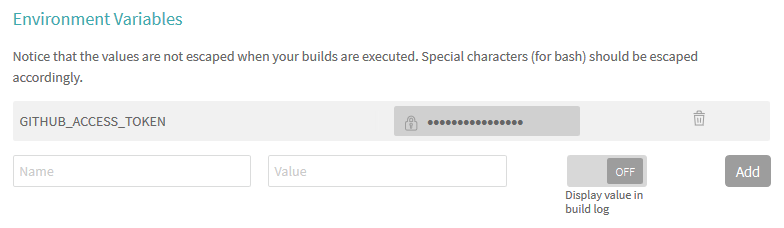
On the same screen, scroll down to the Environment Variables section and create a new variables named GITHUB_ACCESS_TOKEN and in the value field paste a copy of the GitHub personal access token your created earlier and click the 'Add' button.
Finally, create a .travis.yml configuration file in the root of your repository with the following contents
language: node_js
node_js:
- '12'
cache:
directories:
- 'node_modules'
branches:
only:
- master
install:
- npm install
- npm run generate
script:
- echo "Skipping tests"
deploy:
provider: pages
skip-cleanup: true
github-token: $GITHUB_ACCESS_TOKEN # Set in travis-ci.org dashboard, marked secure https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/deployment/pages/#Setting-the-GitHub-token
target-branch: gh-pages
local-dir: dist
on:
branch: master
and then commit this to your repository
git add .travis.yml
git commit -m "Adding travis deploy configuration"
git push origin
Now, whenever you commit any changes to your repository, from within Travis, you'll see a new build start up
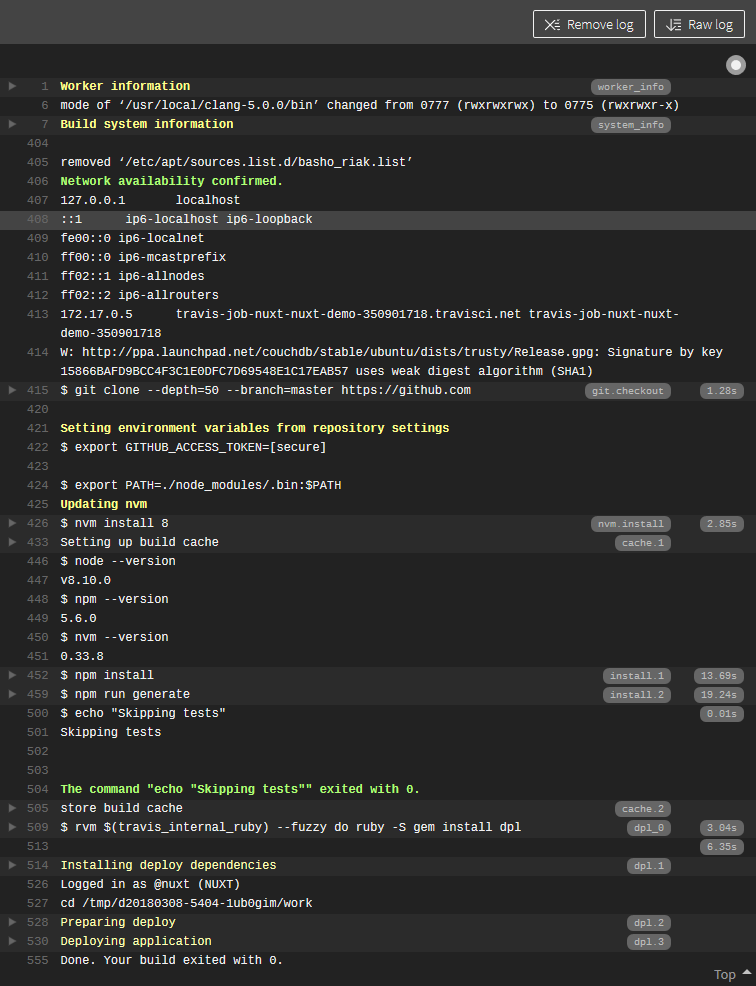
and on completion, you'll see your GitHub pages site automatically updated.
Appveyor
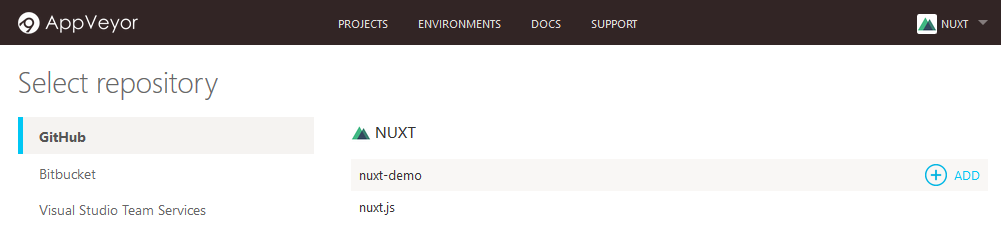
To deploy via Appveyor , another free for open source projects build server, sign up for a new account choosing the GitHub authentication option to sign in using your GitHub account.
Once signed in, click the 'New project' link and then click the 'Add' button beside your repository name in the list displayed to enable the build server on your repository.
Next, in the root of your repository, create an appveyor.yml configuration file with the following contents
environment:
# Nuxt requires node v12 minimum
nodejs_version: '12'
# Encrypt sensitive data (https://ci.appveyor.com/tools/encrypt)
github_access_token:
secure: ENCRYPTED_GITHUB_ACCESS_TOKEN
github_email:
secure: ENCRYPTED_GITHUB_EMAIL
# Only run on master branch
branches:
only:
- master
# Install scripts. (runs after repo cloning)
install:
# switch nodejs version
- ps: Install-Product node $env:nodejs_version
# install modules
- npm install
# generate static files
- npm run generate
# configure global git credentials store (https://www.appveyor.com/docs/how-to/git-push/)
- git config --global credential.helper store
- ps: Add-Content "$env:USERPROFILE\.git-credentials" "https://$($env:github_access_token):x-oauth-basic@github.com`n"
- git config --global user.email $env:github_email
# deploy to GitHub pages
- npm run deploy
# No tests to run
test: off
# Don't actually build.
build: off
NB This configuration assumes you've configured your package.json file as per the Command line deployment instructions
Before you commit this file however, you'll need to change the ENCRYPTED_GITHUB_ACCESS_TOKEN and ENCRYPTED_GITHUB_EMAIL variables with your GitHub personal access token from earlier and your GitHub email address, encrypted using the Appveyor encryption tool .
Once updated, commit the file to your repository
git add appveyor.yml
git commit -m "Adding appveyor deploy configuration"
git push origin
Now, whenever you commit any changes to your repository, from within Appveyor, you'll see a new build start up
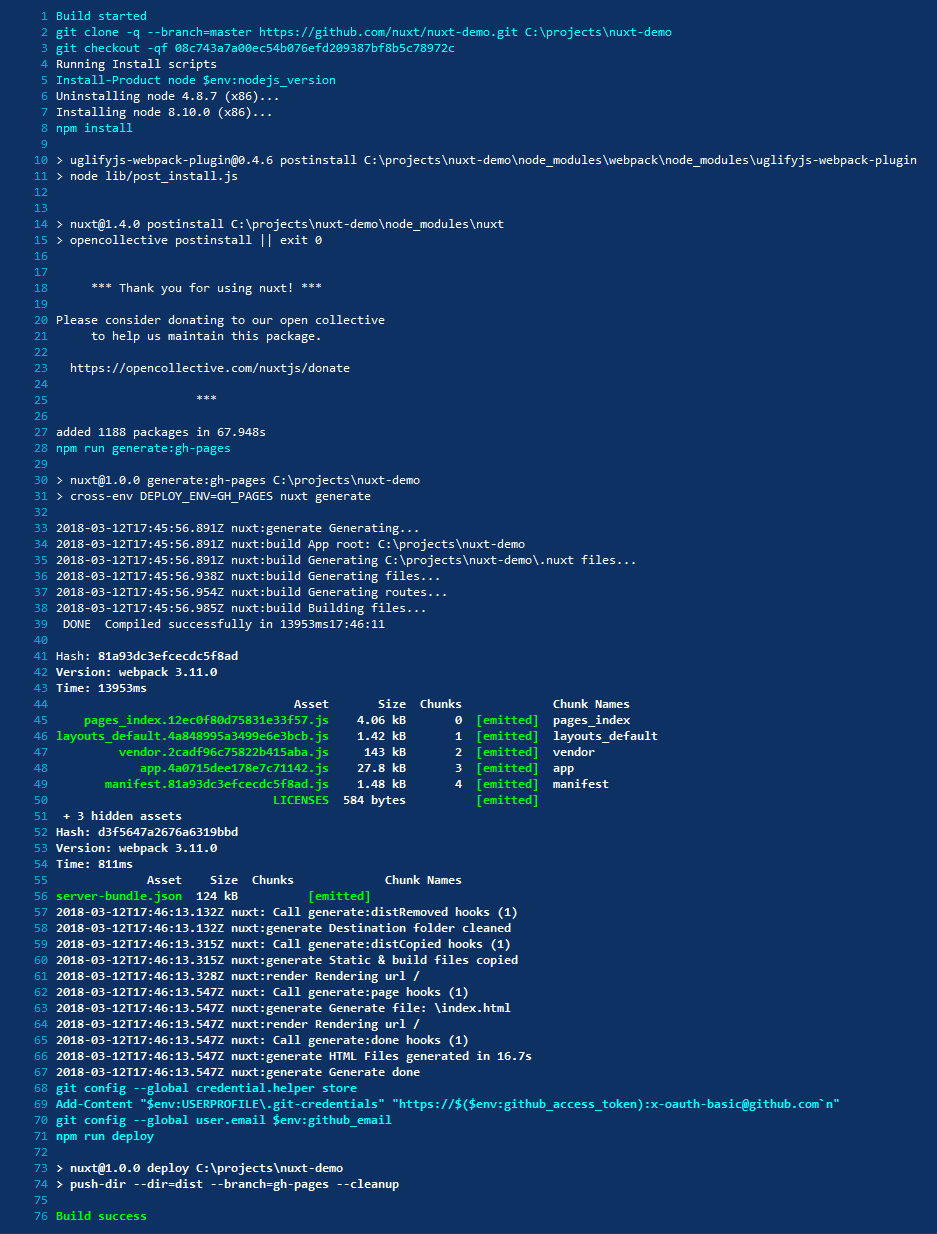
and on completion, you'll see your GitHub pages site automatically updated.
 Sébastien Chopin
Sébastien Chopin
 川音리오
川音리오
 Maciek Palmowski
Maciek Palmowski
 Nestor Vera
Nestor Vera
 Daniel Roe
Daniel Roe
 Yue Yang
Yue Yang
 Jeronimas
Jeronimas
 Clément Ollivier
Clément Ollivier
 Alexander Lichter
Alexander Lichter
 N3-rd
N3-rd
 Adrien Zaganelli
Adrien Zaganelli
 Mag
Mag
 Stefan Huber
Stefan Huber
 Olga Bulat
Olga Bulat
 Paiva
Paiva
 Florian Reuschel
Florian Reuschel
 Rishi Raj Jain
Rishi Raj Jain
 Savas Vedova
Savas Vedova
 Steven Soekha
Steven Soekha
 Vinícius Alves
Vinícius Alves
 Kareem Dabbeet
Kareem Dabbeet
 Valentín Costa
Valentín Costa
 Ryan Skinner
Ryan Skinner
 Alex Hirzel
Alex Hirzel
 Ajeet Chaulagain
Ajeet Chaulagain
 René Eschke
René Eschke
 Nico Devs
Nico Devs
 Muhammad Bin Shehzad
Muhammad Bin Shehzad
 Nazaré da Piedade
Nazaré da Piedade
 Naoki Hamada
Naoki Hamada
 Tom
Tom
 Yann Aufray
Yann Aufray
 Anthony Chu
Anthony Chu
 Nuzhat Minhaz
Nuzhat Minhaz
 Lucas Portet
Lucas Portet
 Richard Schloss
Richard Schloss
 Bobby
Bobby
 bpy
bpy
 Antony Konstantinidis
Antony Konstantinidis
 Hibariya
Hibariya
 Jose Seabra
Jose Seabra
 Eze
Eze
 Florian Lefebvre
Florian Lefebvre
 Lucas Recoaro
Lucas Recoaro
 Julien SEIXAS
Julien SEIXAS
 Sylvain Marroufin
Sylvain Marroufin
 Spencer Cooley
Spencer Cooley
 Piotr Zatorski
Piotr Zatorski
 Vladimir Semyonov
Vladimir Semyonov
 Harry Allen
Harry Allen
 kazuya kawaguchi
kazuya kawaguchi